Four Major Rivers Research Centers
- Effect of Aquatic Macrophyte on Water Environment of Lake Paldang
We comprehensively investigated the effect of aquatic plant communities on water quality and aquatic ecosystems in Paldang Lake. In 2021, we surveyed and compared water quality and aquatic ecosystems inside and outside water chestnut and lotus communities. Although we observed no significant difference in water quality between the inside and outside of the communities, we observed an increase in turbidity, TP, and chlorophyll a (Chl.a) in some water chestnut communities. The number of species and population density of phytoplankton, zooplankton and aquatic insects were higher inside the aquatic plant colonies than outside, indicating that aquatic plant communities provide habitats for various organisms. We also investigated odor substances and the amount of odor substance-producing gene; 2-MIB* concentrations and the amount of 2-MIB-generating gene were higher inside the water chestnut communities than outside. Further, the amount of 2-MIB-generating gene were higher on the surface of water chestnut than lotus. Moreover, we observed a phenomenon that cyanobacteria become trapped in water chestnut communities and cannot move with the flow of water, demonstrating the potential for water chestnut to induce an increase in odor substances. We also developed a 2-MIB real-time PCR** analysis method to verify the occurrence probability of odorous substances in Paldang Lake.

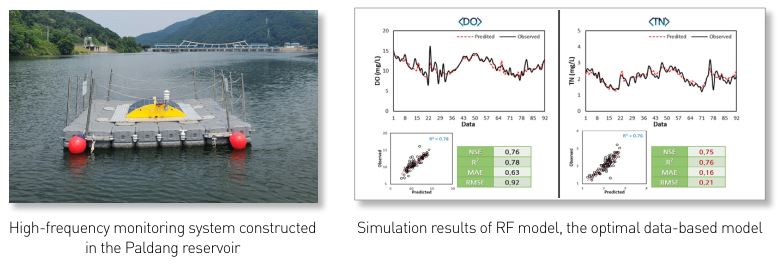
- Prediction on water quality variations in Paldang reservoir by climate change(Ⅰ) - Application of databased model through high frequency monitoring
Water flowing from the South and North Han Rivers and Gyeongancheon meet at the Paldang reservoir, a water source for residents in the Seoul metropolitan area. Hence, due to the large spatio-temporal fluctuations, it is critical to understand its characteristics and change patterns. This study implemented and operated a high-frequency monitoring system in the Paldang reservoir water source and predicted water quality according to climate change using a data-based model. The predicting accuracy of changes in water quality according to water depth in the Paldang reservoir improved when conducting simulations using meteorological, flow rate, and water quality data of the surface, middle, and lower layers. In particular, we yielded excellent predicting results for dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration (NSE 0.95 in the Random Forest model), and optimal models were derived with Random Forest (RF), eXtreme Gradient Boost (XGB), and deep neural network. Next year, we also plan to utilize high-frequency data in the three optimal models to predict long- and short-term changes in water quality according to climate factors. We expect the model accuracy to improve with highfrequency data in units of hours and days.
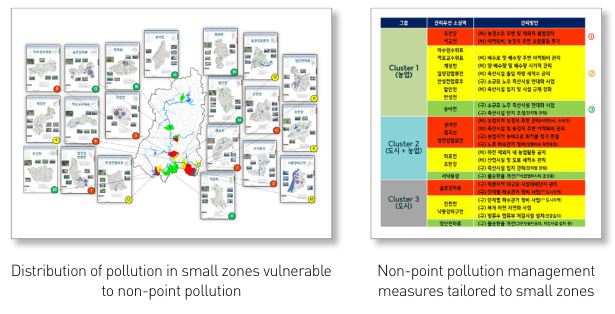
- A Study on best management of critical source areas with nonpoint pollution according to climate change(Ⅰ)
In 195 small zones of the Nakdong River system, we conducted a vulnerability assessment of non-point pollution sources according to future climate changes and determined management priorities based on the environmental variables of non-point pollution sources derived from prior research. We used six variables in the vulnerability assessment (future precipitation, nonpoint load, impervious area, runoff curve number, water quality, and excess rate of water quality standard). Each variable was normalized* and indexed, the percentage values were summed, and each was ranked. In the case of the upper small zones, we captured aerial images and performed field surveys to identify the distributions of non-point pollution sources and issues and explore corresponding solutions. According to land use characteristics, we examined the operation methods of agricultural drainage ditches, the distribution of livestock farms, and the ratio of separated sewer systems, identified problems, and established appropriate management measures.
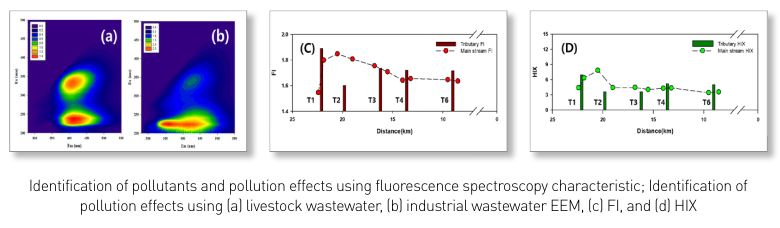
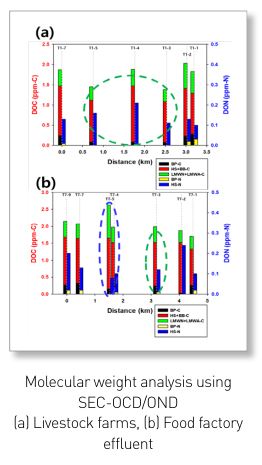
- Investigation on the origin of organic pollutants in the upstream of Mihostream and management strategies for the corresponding small watersheds(Ⅱ)
Through a two-year survey of the upstream watershed of Mihocheon, we found that the BOD concentrations of the mainstream and inflow streams have decreased overall, whereas livestock pollutants showed an increasing trend. Through this study, we could classify organic pollutants in rivers using various fluorescence spectroscopic characteristics, which enabled us to identify the scope of the pollutants’ impact on the tributaries and mainstream. After rapidly identifying specific pollutants via fluorescence analysis, it was possible to identify the characteristics of organic pollutants in connection with SEC-OCD/OND more effectively. We derived structural measures for installing constructed wetlands in Natgeoreumcheon and Jungsancheon watersheds and installing livestock manure public sewage treatment facilities in connection with public sewage treatment facilities in Mihocheon. For non-structural measures, we proposed livestock manure collection, agricultural drainage manamgement, nutrient management and activation of local governance.
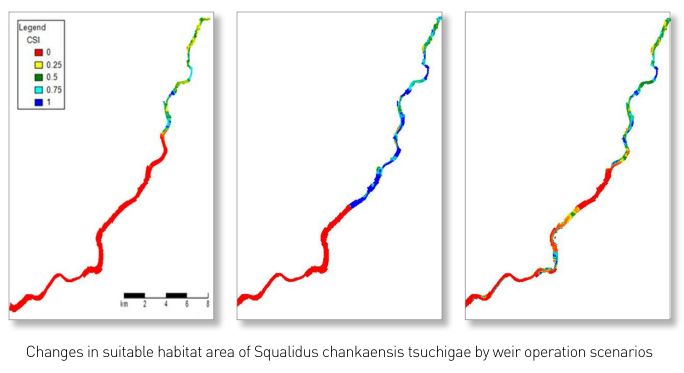
- Application of habitat analysis and modelling for improvement of aquatic ecosystem health in the Yeongsan River(II)
To predict and efficiently manage changes in aquatic ecosystems caused by environmental changes, a model that integrates and analyzes the interactions between physical, chemical, and biological factors is necessary. For this purpose, we combined the 3D hydraulic and water quality model Delft3D and the aquatic ecology model HABITAT to build an integrated hydraulicwater quality-aquatic ecology prediction model applicable to the Yeongsan River system. Based on field survey data of the Yeongsan River system, we constructed habitat suitability curves for each species according to physical and chemical factors and simulated changes in habitat suitability caused by weir operation for Squalidus chankaensis tsuchigae, Cyprinus carpio, and Micropterus salmoides. We also calculated the changes in average suitable habitat area of target fish species and analyzed the tolerance level of occurring fish species to changes in the physical environment.
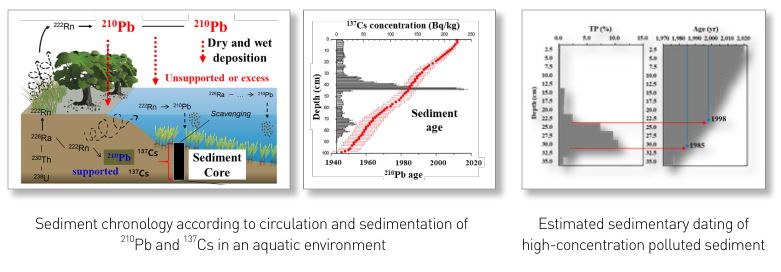
- A study on the chronology of lake sediments using radioisotope techniques
Sediment chronology is a very useful tool for verifying historical pollution records using artificial (e.g., 137 Cs) and natural (e.g., 210 Pb) radioisotopes from sediment cores. This study was conducted to establish a research foundation for sediment chronology techniques and apply them to agricultural reservoirs to assess the pollution sources of polluted sediments. By establishing a specimen preparation technique for radioisotopes ( 210 Pb, 226 Ra) analysis and a customized simple calibration method, we laid the foundation for research on sediment chronology. We could estimate the sedimentary dating of polluted sediments by applying the vertical distributions of radioisotope concentrations obtained from this method to the sediment chronology model. We have presented the research findings as evidence for identifying the scientific causes of polluted sediments. In the future, this techinque can be applied to sediment management policies to assess the cause of polluted sediments.
|